Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Cd
Cd鈴井 伸郎; 石川 覚*; 伊藤 小百合*; 石井 里美; 井倉 将人*; 安部 匡*; 倉俣 正人*; 河地 有木; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
In this study, we have developed direct imaging of  Cd in underground parts using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS), and applied the method to analyse the time-varying distribution of Cd in the high- and low-Cd accumulating rice cultivars. The hydroponic culture solution including
Cd in underground parts using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS), and applied the method to analyse the time-varying distribution of Cd in the high- and low-Cd accumulating rice cultivars. The hydroponic culture solution including  Cd were fed to the six individual cultivars, and the serial images of the
Cd were fed to the six individual cultivars, and the serial images of the  Cd distribution in the both underground and aerial parts were obtained for 24 h using PETIS and newly developed method of direct imaging of
Cd distribution in the both underground and aerial parts were obtained for 24 h using PETIS and newly developed method of direct imaging of  Cd root uptake. As a result, the serial images of
Cd root uptake. As a result, the serial images of  Cd uptake by the roots of rice cultivars was successfully obtained. Time courses of Cd amounts demonstrated that decrease of Cd in the culture solution was similar but retention of Cd in the roots was drastically different between the high- and low-Cd accumulating cultivars. The low-Cd accumulating cultivars showed rapid saturation curves of Cd amount in the roots, whereas the high-Cd accumulating cultivars were characterized by curves with a peak within 30 min after
Cd uptake by the roots of rice cultivars was successfully obtained. Time courses of Cd amounts demonstrated that decrease of Cd in the culture solution was similar but retention of Cd in the roots was drastically different between the high- and low-Cd accumulating cultivars. The low-Cd accumulating cultivars showed rapid saturation curves of Cd amount in the roots, whereas the high-Cd accumulating cultivars were characterized by curves with a peak within 30 min after  Cd supplementation, and a subsequent steep decrease. These results indicate that the high-Cd accumulating cultivars have a less ability to retain Cd in the root tissue compared with the low-Cd accumulating cultivars, resulting in higher Cd accumulation in the shoots.
Cd supplementation, and a subsequent steep decrease. These results indicate that the high-Cd accumulating cultivars have a less ability to retain Cd in the root tissue compared with the low-Cd accumulating cultivars, resulting in higher Cd accumulation in the shoots.
中村 進一*; 鈴井 伸郎; 尹 永根; 石井 里美; 河地 有木; 頼 泰樹*; 服部 浩之*; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
In our previous work, we confirmed that glutathione (GSH), applied to roots, reduced Cd accumulation in the shoot of oilseed rape plants selectively. However, the molecular mechanisms of this phenomenon are not fully understood so far. In this work, we investigated effects of GSH, applied to roots, on Cd behaviors in plants by dividing roots into two parts and dipping these roots in different hydroponic solutions. Three-week old oilseed rape plants were set by dividing their roots into two parts. Cd was added to one side of the nutrient solution, and GSH was added to another side of the solution. After harvest, Cd content in each part of seedling was measured by using an atomic absorption photometer. As a result, there were significant differences in Cd distribution ratio of Cd treated roots and plant shoots between control plants and GSH treated plants. GSH, applied to another side of roots, decreased Cd transport from Cd treated roots to other parts of the plants. We also succeeded to obtain serial images of  Cd movement from one side of the nutrient solution to roots in another side using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). Our experimental results suggested that some signals, triggered by GSH, might be transported via vascular tissues and playing an import role in distributing Cd in the plant body.
Cd movement from one side of the nutrient solution to roots in another side using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). Our experimental results suggested that some signals, triggered by GSH, might be transported via vascular tissues and playing an import role in distributing Cd in the plant body.
浦口 晋平*; 鈴井 伸郎; 神谷 岳洋*; 尹 永根; 石井 里美; 藤巻 秀; 藤原 徹*
no journal, ,
Reducing cadmium (Cd) contents in cereal grains is significant to prevent a risk of Cd toxicity to human health. In rice, understanding of Cd transport mechanisms has been advanced recently. We have demonstrated that OsLCT1 (low-affinity cation transporter is an efflux Cd-transporter on the plasma membrane and is responsible for Cd transport toward grains in a standard japonica rice (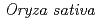 L. cv. Nipponbare). Generally,
L. cv. Nipponbare). Generally, 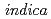 cultivars show higher Cd accumulation in shoot and grains. However, molecular understanding of Cd transporters in indica rice is still insufficient. In this study, we isolated
cultivars show higher Cd accumulation in shoot and grains. However, molecular understanding of Cd transporters in indica rice is still insufficient. In this study, we isolated 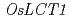 cDNA from cv. Kasalath, a model
cDNA from cv. Kasalath, a model 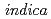 cultivar and characterized the cadmium transport activity of the OsLCT1 allele from Kasalath in the yeast assay system. As a result, the sequence variations found between Nipponbare and Kasalath OsLCT1 do not affect the Cd transport activity mediated by OsLCT1. In the presentation, we will also present the results of Cd dynamics using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system, and discuss physiological roles of OsLCT1 in Cd transport through nodes to grains.
cultivar and characterized the cadmium transport activity of the OsLCT1 allele from Kasalath in the yeast assay system. As a result, the sequence variations found between Nipponbare and Kasalath OsLCT1 do not affect the Cd transport activity mediated by OsLCT1. In the presentation, we will also present the results of Cd dynamics using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system, and discuss physiological roles of OsLCT1 in Cd transport through nodes to grains.
河地 有木; 小柳 淳*; 鈴井 伸郎; 石井 里美; 尹 永根; 岩崎 郁*; 小川 健一*; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
We have developed a method based on  CO
CO tracer gas and the positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS) to evaluate individual photosynthetic abilities of young plant seedlings planted collectively on a petri dish with agar medium, for analysis studies on effects of genetic modification or treatment of chemical agents on enhancing plant biomass. As a result of evaluation experiments,
tracer gas and the positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS) to evaluate individual photosynthetic abilities of young plant seedlings planted collectively on a petri dish with agar medium, for analysis studies on effects of genetic modification or treatment of chemical agents on enhancing plant biomass. As a result of evaluation experiments,  C-images with little variation among the plants were obtained, and the average rate of carbon fixation by wild-type plants was estimated only with approximately 6% of standard error through a mathematical analysis, which proved the good quantitative capability of this experimental system and analysis method for evaluation of a genetically homogenous line. Then, eight plants of ch1-1 mutant, which lacks chlorophyll b and has lower carbon fixation activity, were also subjected to this method together with eight wild-type plants. It was estimated that ch1-1 mutants has a carbon fixation rate approximately 52.6
C-images with little variation among the plants were obtained, and the average rate of carbon fixation by wild-type plants was estimated only with approximately 6% of standard error through a mathematical analysis, which proved the good quantitative capability of this experimental system and analysis method for evaluation of a genetically homogenous line. Then, eight plants of ch1-1 mutant, which lacks chlorophyll b and has lower carbon fixation activity, were also subjected to this method together with eight wild-type plants. It was estimated that ch1-1 mutants has a carbon fixation rate approximately 52.6  4.1% lower than that of wild-type in average. In conclusion, we realized a method of quantitative and statistical evaluation of carbon fixation for small plant individuals, by using PETIS.
4.1% lower than that of wild-type in average. In conclusion, we realized a method of quantitative and statistical evaluation of carbon fixation for small plant individuals, by using PETIS.
河地 有木; 鈴井 伸郎; 石井 里美; 石岡 典子; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
The positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS) and caron-11-labeled carbon dioxide ( CO
CO ) can image carbon movement during photoassimilation and export in a plant leaf, and
) can image carbon movement during photoassimilation and export in a plant leaf, and  C kinetics make it possible to estimate physiological function parameters in those processes. With an exposure
C kinetics make it possible to estimate physiological function parameters in those processes. With an exposure  CO
CO -gas to a leaf, PETIS experiments were performed under three light conditions on a single leaf. In order to estimate the rate constants of photoassimilation parameters, time activity curves of
-gas to a leaf, PETIS experiments were performed under three light conditions on a single leaf. In order to estimate the rate constants of photoassimilation parameters, time activity curves of  CO
CO gas input and leaf response were fitted to an appropriate compartmental tracer kinetic model, which applies influx and efflux for photoassimilation and photosynthate export rate constants. These results are reasonable response against light environment respectively. Kinetic parameters are fitted enough with pixel-by-pixel analysis, so that our method suggest that a parametric imaging of photosynthesis, which is indicative of a functional-imaging analysis in plant study.
gas input and leaf response were fitted to an appropriate compartmental tracer kinetic model, which applies influx and efflux for photoassimilation and photosynthate export rate constants. These results are reasonable response against light environment respectively. Kinetic parameters are fitted enough with pixel-by-pixel analysis, so that our method suggest that a parametric imaging of photosynthesis, which is indicative of a functional-imaging analysis in plant study.
藤巻 秀; 河地 有木; 尹 永根; 鈴井 伸郎; 石井 里美; 渡部 浩司*; 山本 誠一*
no journal, ,
A variety of agricultural studies, such as fertilizer management and plant breeding, are undertaken intensively for reduction of radiocesium uptake in crops, or, enhancement of uptake in phytoremediation in Japan. Now we are going to introduce a new "eye" to this exploration. That is a potential method to observe the movement of radiocesium in a living plant like a video camera without sampling of the plant tissues. We have ever established a live-imaging method for studies on cadmium by using the positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS), and successfully revealed cadmium dynamics in various plants. However, PETIS is applicable to neither Cs-134 nor Cs-137 because they do not emit positrons. In this study, we are establishing another new system especially designed for plant studies on radiocesium based on the principle of the "gamma camera", and have already obtained some results with intact crops.
菊地 郁*; 石井 里美; 河地 有木; 鈴井 伸郎; 藤巻 秀
no journal, ,
In the eggplant cultivation, defoliation is normally used to prevent the disease and insect as well as to raise the efficiency of light interception for efficient fruit production. However, the general guideline for defoliation is not established yet because fundamental knowledge about effects of defoliation on the nutritional balance in individuals has hardly been obtained. For these reason, it is important to clarify the translocation mechanism of the photoassimilates from each leaf to the fruit in eggplant. Previously, we succeeded in observation of translocation of  C-labeled photoassimilates from a leaf into a fruit and established a method for the quantitative analysis of the translocation rates and velocities using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). PETIS can noninvasively visualize the movement of
C-labeled photoassimilates from a leaf into a fruit and established a method for the quantitative analysis of the translocation rates and velocities using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). PETIS can noninvasively visualize the movement of  C-labeled photoassimilates in plants, and thus repetitive experiments with one plant are possible due to the short half-life (20 min) of
C-labeled photoassimilates in plants, and thus repetitive experiments with one plant are possible due to the short half-life (20 min) of  C. In this study, we analyzed translocation of photoassimilates in eggplant from each of the three major neighboring leaves to a fruit of interest, and estimated the respective contributions to the fruit growth using
C. In this study, we analyzed translocation of photoassimilates in eggplant from each of the three major neighboring leaves to a fruit of interest, and estimated the respective contributions to the fruit growth using  CO
CO and PETIS.
and PETIS.